What is the temperature variation within earths crust. or Describe the temperature inside the earths crust.
1 Answer
The places where earthquake and volcanic eruption are frequent , there is increase in 80 °C per kilometre depth but at other places it is 30°C per kilometre in the earth crust.
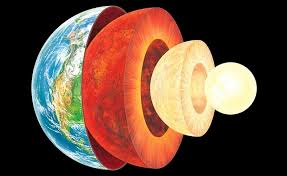
The crust is made of solid rocks and minerals. Beneath the crust is the mantle, which is also mostly solid rocks and minerals, but punctuated by malleable areas of semi-solid magma. At the center of the Earth is a hot, dense metal core.They are, in order from the exterior to the interior – the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core.The core is the thickest layer of the Earth, and the crust is relatively thin, compared to the other layers.
The Earth's interior is composed of four layers, three solid and one liquid—not magma but molten metal, nearly as hot as the surface of the sun. The deepest layer is a solid iron ball, about 1,500 miles (2,400 kilometers) in diameter. ... Above the inner core is the outer core, a shell of liquid iron.
The temperature is around 1000°C at the base of the crust, around 3500°C at the base of the mantle, and around 5,000°C at Earth's centre. The temperature gradient within the lithosphere (upper 100 km) is quite variable depending on the tectonic setting.As you head toward the center of the Earth, temperatures increase exponentially. The Earth's core is a sphere of molten nickel and iron. ... As you move further and further away from the core, the crust cools to much colder temperatures all the way up to the surface. The Earth gets hotter as you move towards to center.
The temperature of Earth's interior affects everything from the movement of tectonic plates to the formation of the planet. ... "Rock from the upper mantle slowly rises to fill the void between the plates, melting as the pressure decreases, then cooling and re-solidifying to form new crust along the ocean bottom.