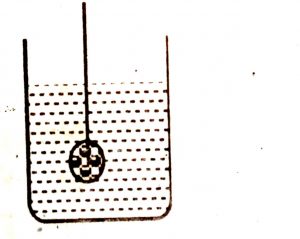
The figure shows a small iron ball sunk in a beaker of fresh water. Now, if some table salt is added to water in the beaker, explain how an upthrust experienced by the ball will be affected.
1 Answer
Given figure shows iron ball sunk in a fresh water and if table salt is added to fresh water its density increases, ultimately upthrust of salty water increases to iron ball and iron ball slightly moves upwards or sinks less in the given solution.
The iron ball has a greater density than water so the gravitational force applied is greater on it than the buoyant force. Hence, it sinks. Whereas, a rubber ball has a lesser density than water. So, the opposing buoyant force is greater and since the ball floats. There will be no flow of heat either from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball since both water and iron ball are at same temperatures so heat transfer will not take place.Iron's density is 7.9 g/cm³ (grams per cubic centimeter). Mercury's density is 13.5 g/cm³. The iron presses on the mercury, but because it is lighter, it floats. There will be some submersion, however, even as a boat floats on water, but part of it rests within the water
The weight of liquid displaced is the weight of the liquid that has been replaced by the object. The volume of this amount of liquid is equal to the volume of the object itself. The weight of fluid displaced and therefore the upthrust will be bigger if the density of the liquid is large. The upthrust in salty water (relative density = 1.1) is larger than that in water (relative density = 1.0) for the same object. This is why it is easier to swim in the sea than in a freshwater lake.Upthrust = apparent loss of weight of object = weight in air - weight in liquid.
Archimedes principle says that when an object is immersed in a liquid the apparent loss of weight of an object is equal to the upthrust and this is also equal to the weight of the liquid displaced. You can prove this by the following experiments.
Weigh an object in air and then lower it into a beaker of water that is resting on a top pan balance. The reading on the spring balance will get less while the reading on the top pan balance will increase by the same amount.
If you already know the density of the liquid then you can simply measure the volume of displaced water and use mass = volume x density to find its mass. This can easily be done using a measuring cylinder as shown in the diagram.
You can see how the apparent weight of the stone gets less when it is immersed in water. If it was only partly immersed it would appear to weigh less than in air but not as little as when it is totally immersed in the water.
