Define tissue and describe in detail about structure and function of complex permanent tissues with suitable diagram.
1 Answer
Tissue is a group of similar or dissimilar cells having a common origin, similar structure, and common methods of development as well as a similar set of functions. There are two types of tissues found in plants and they are known as meristematic tissues and permanent tissues.
The Monocot Stem
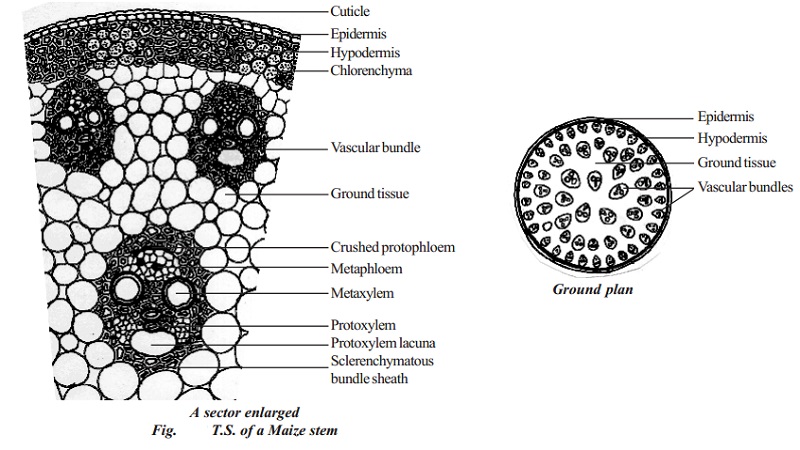
- Epidermis: It is the outermost single layer of compactly arranged elongated barrel-shaped, transparent parenchymatous tissues without intercellular spaces. Externally it is covered by a cuticle. At some places, the epidermis contains stomata for gaseous exchange. Each stoma has two dumbbell-shaped guard cells.
- Hypodermis: It is 2-3 layered thick, dead lignified sclerenchymatous tissue that lies below the epidermis. It provides rigidity and mechanical strength to the stem.
- Ground tissues: It has no differentiation of cortex, endodermis, pericycle, pith, and medullary rays (except Asparagus). It is parenchymatous and occupies the whole stem interior. The cells are small and angular towards the hypodermis and become large and oval in the inner region. The ground tissue stores food. Some cells involve in photosynthesis due to chloroplast in them.
- Vascular Strand: Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissue. They are collateral and closed type. The bundles towards the periphery are greater in number and smaller in size than those towards the bundle sheath is more conspicuous toward the upper and lower sides of the bundles. The vascular bundle consists of phloem towards the outer side and xylem towards pitched and bigger vessels of metaxylem and smaller and annular or spinal vessels of protoxylem. Some of the protoxylem vessels and xylem parenchyma cells dissolve and form a cavity that generally stores water and is called a water cavity or lysogenous cavity.
- Medullary rays: It is absent in monocot stem
- Pith: It is not well marked
Why secondary growth does not take place?
Normally, the vascular bundles of the monocotyledons stems are closed ones. Thus due to the absence of the cambium, they lack secondary growth in thickness and the vascular system is wholly composed of primary tissues. The bundles remain irregularly scattered in the ground tissues, forming an atactostele, where the limits of the cortex and other ground tissues can be hardly discerned.