What products would you expect at cathode and anode when aqueous NaCl is electrolysed using platinum electrode ?
1 Answer
The water competes with the dissolved Na+ and Cl ions because of the oxidization and reduction property of water, as a result, hydrogen is produced instead of sodium.
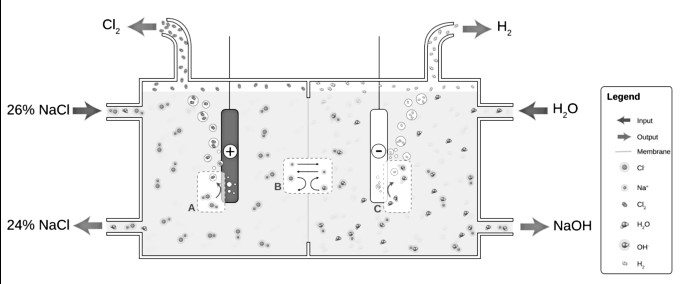
The electrolysis of aqueous NaCl results in hydrogen and chlorine gas. At the anode (A), chloride (Cl-) is oxidized to chlorine. The ion-selective membrane (B) allows the counterion Na+ to freely flow across but prevents anions such as hydroxide (OH-) and chloride from diffusing across. At the cathode (C), water is reduced to hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The net process is the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of NaCl into industrially useful products sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and chlorine gas.
The reaction at Cathode is
\(H_2O(l)+2e^-\rightarrow H_2(g)+2OH^-\)
While the reaction at Anode is
\(Cl^-\rightarrow\frac12Cl_2(g)+1e^-\)
The overall reaction is as follows:
\(NaCl(aq)+H_2O(l)\rightarrow Na^+(aq)+OH^-(aq)+H_2(g)+\frac12Cl_2(g)\)
Reduction of Na+ (E° = –2.7 v) is energetically more difficult than the reduction of water (–1.23 v), so in aqueous solution, the latter will prevail.
-
How would you predict the geometry of the ammonia molecule on the basis of VSEPR theory? 1
-
What kind of hybridization results in trigonal planer geometry? 1
-
Which hybridization results in a linear geometry. Give an example. 1
-
What kind of hybridization results in tetrahedral geometry? Give an example. 1
-
What is the mode of hybridization for carbon in ethyne and oxygen in water? 1
-
Predict the mode of hybridization of B in BF3. write two features. 1
-
State any two proper conditions and mode of hybridization of C in C2H2? 1