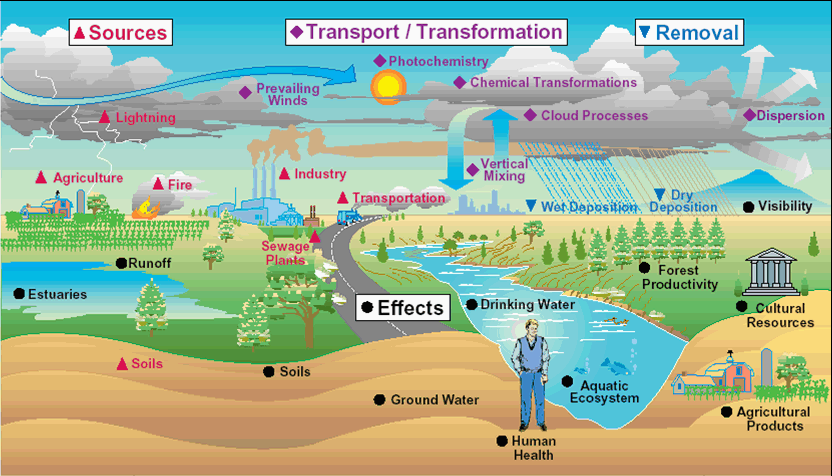
What are primary pollutants? Write with examples.
1 Answer
The pollutants with originate directly from the source is called primary pollutants. For example sulphur dioxide, nitric oxide, ammonia, hydrogen sulphide, etc. In contrast to secondary pollutants which must form in the atmosphere, secondary pollutants directly form in the source such as coal operated power plants, biomass burning, natural forest fires, bush fires, volcanoes and many more. Primary pollutants are not just harmful to humans, plants, animals and overall environment they are also responsible in the formation of the secondary pollutants.
One of the good things about primary pollutants is that its emission has been heavily controlled because of improved usages rules and regulations, economic changes and technological advancement. Noticeable types of pollutants are
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx): Nitrogen dioxide are highly toxic to vegetation. They can also cause increased greenhouse effects. On top of that it is also major component of acid rain. Excess Nitrogen oxide accelerates the growth of algae which can reduce amount of oxygen dissolved in the water making it very difficult for aquatic life.
- Carbon monoxide (CO): Carbon monoxide is formed due to incomplete combustion of fuels such as propane, natural gas, gasoline, oil, coal, or wood. Even though carbon monoxide doesn't heavily impact on environment, its reaction with other pollutants can have huge impact on ozone layer depletion. Besides, carbon monoxide is extremely dangerous to human health if inhaled. It reduces bloods ability to carry oxygen. High exposure can cause dizziness, chest pain, blurred vision and even suffocation to death.
- Volatile organic substance (VOCs): These are organic molecules mainly hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are one of the worst kind of pollution human kind have ever designed. Now we consider them volatile because when exposed to heat they quickly evaporate into the atmosphere.
- Sulfur oxides (SOx): Sulfur oxides can have negative effects on overall vegetation including agricultural crops. Higher exposure to sulfur oxides cause plants to lose leaves, have a lower production, or even die prematurely. It can also be harmful to human health by reducing lung function, increasing respiratory diseases, irritation, of the eyes, nose, and throat and even death.
- particulate matter (PM): The mixtures of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air is called particulate matter. Examples are dust, dirt, soot, coal ash and smoke thick enough visible to human eyes. Some particulate matters are extremely small and need microscope to see them. Particulate matters can cause significant health problems in humans. They reduce breathing capacity by penetrating deep into lungs. Long exposure to PM can cause cardiovascular and respiratory disease and even lungs cancer.