Discuss an experiment to demonstrate the root pressure of a plant.
1 Answer
Demonstrate the process of root pressure
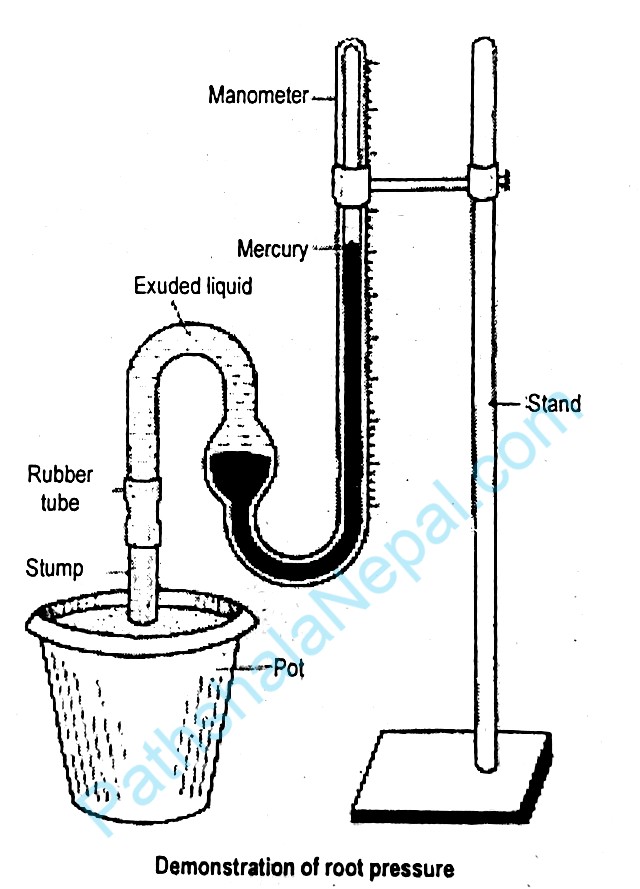
Apparatus required: A well-watered herbaceous plant, a knife, a rubber tube, a narrow glass tube and colored water, manometer, etc.
Theory: Root pressure is defined as hydrostatic pressure developed in the root due to the accumulation of absorbed water. If the pressure exerted on the liquid contents of the cortical cells of the roots, under fully turgid conditions this root pressure pushes the water up the xylem vessels to the aerial parts. It shows that water absorption is an active process.
Procedure: Water a potted herbaceous plant. Keep it overnight. The next morning, cut off the stem a few centimeters above the soil level or near to the root. Fix a long and narrow glass tube to the cut end of the stump with the help of rubber tubing. Pour a little colored water into the glass tube and mark its level. The glass tube is connected to a manometer and the whole setup is then leaf for observation.
Observation: After some time, the level of the colored water rises in the level of the mercury of the monometer shows the measurement of root pressure.
Result and conclusion: A rise in the level of water in the glass tube is due to the pressure exerted by water exuded from the cut part of the stem. The exuding of water from the cut end of the stem is called bleeding. The flow of water from the cut surface or bleeding when measured by mercury manometer is estimated to 3-5 atmospheres only.
Precautions:
- The plants should be well watered but the soil should not be flooded
- The soil should not be deficient in minerals.
- Place the apparatus in a cool and humid environment.
- Evaporation from the open end of the tube is prevented by using non-drying oil or the Petri dish.
- The plants should be vigorously growing.