Discuss cohesion-tension theory for the uptake of water.
1 Answer
Most of the water absorbed is lost through the aerial parts of the plants into the air by the process called transpiration. Very little water (less than 2%) is used up in various metabolic activities of plants. Most of the transpiration. Takes place through leaves known as foliar transpiration. Types of transpiration
Transpiration may occur through the cuticle, lenticels stomata, and sometimes bark, and is accordingly called Cuticular, lenticular, stomatal, and bark transpiration.
- Cuticular transpiration: It is the loss of water in the vapor from the general surface (leaves and young stems) through the layer of the cuticle. Cubicula transpiration is appreciable only in case the cuticle is thin as in entophytic plants growing in humid. It continues throughout day and night.
- Stomata Transpiration: it is the loss of water in the form of vapor from the stomata present on the surface of leaves and to a lesser presence on the surface of leaves and to a lesser extent on the surface of flowers and young stem. it is the major part of transpiration (80-90) it, however, occurs only when stomata are open.
- Lenticular transpiration: This is less water in the form of vapor from lenticels or aerating poxes present in the bark of the system.
- Bark transpiration: A small quality of water is lost from the corky bark of the stem. both lenticular and bark transpiration continues day and night time.
Cohesion- Tension Theory or Transpiration Pull Theory
This theory was given by Dixon in 1894. It was further improved by Dixon in 1914. It is also called cohesion and transpiration pull theory or Dixon theory of the ascent of sap. It is the most accepted theory.
The main features of the following theory are as follow-
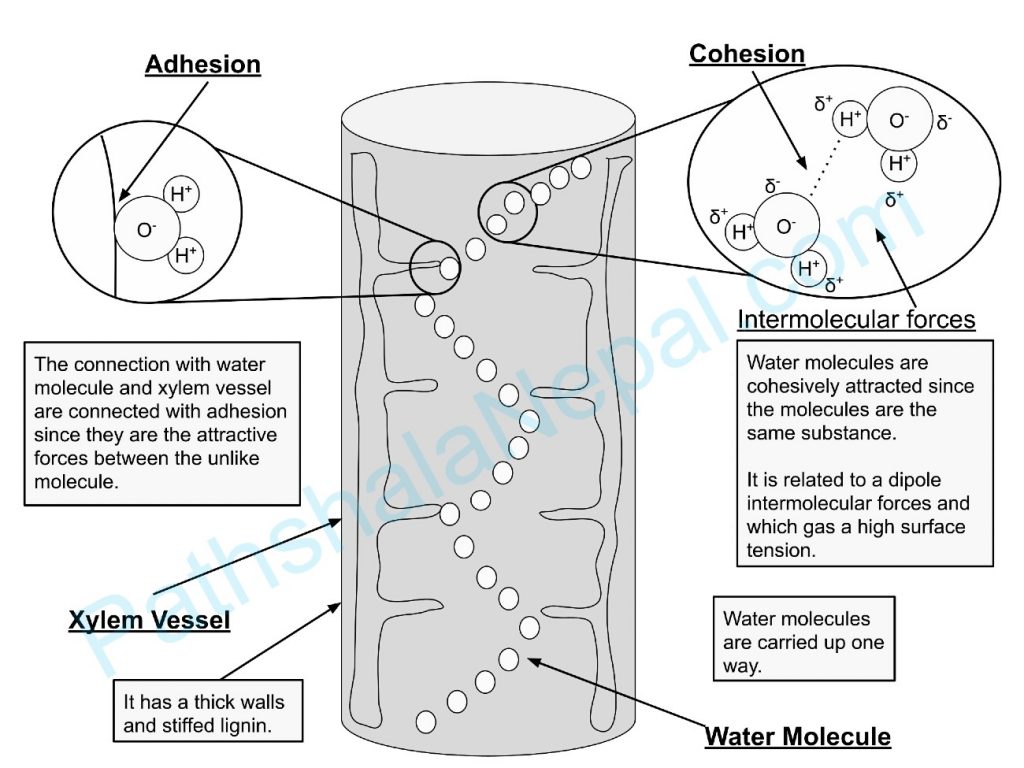
- Cohesion Force: water molecules are held together by strong cohesion force which is due to hydrogen bonds amongst them. There is another force of adhesion that holds water to the walls of xylem channels.
- Continuous Water column: A continuous column of water is present in the xylem channel plants.
- Transpiration Pull: Loss of water the ariel parts of transpiration cause a suction pressure in the water column of the plants. It is known as the transpiration pull. Transpiration pulls lifts the water in the water column of the plant. It is known as the transpiration pull. Transpiration pulls lifts the water upwardly. The continuity of water does not break due to the cohesion force between two water molecules.