Define respiration. Describe in detail the experiment to demonstrate the aerobic respiration with clean diagrams.
1 Answer
Respiration is the physiological process in which complete and incomplete oxidation of organic food takes place. In respiration oxidation of various organic food substances like carbohydrates, may takes place. The process of respiration occurs in all living cells of plants and animals and generally called cellular respiration. The energy produced during the process is used in all the life activities of the organisms. It is a catabolic process that occurs in mitochondria and cytoplasm of the cell and represented by the following chemical equation.
C6H12O6 + 6O2→ 6CO2 + H2O + Energy (2868KJ or 686Kcal)
The main factor associated with respiration are
- Consumption of atmospheric oxygen.
- Release of energy by break down of organic food.
- Liberation of carbon dioxide and a small quantity of water.
- Oxidation and decomposition of reserve food.
Types of respiration: based on the availability of oxygen during the process, respiration can be classified into two types
- Aerobic respiration
Respiration which occurs in the presence of oxygen and organic food materials is completely oxidized into CO2 and H2O wit the release of energy is called aerobic respiration.
C6H12O6 + 6O+2→ 6CO2 + H2O + Energy (2868KJ or 686Kcal)
- Anaerobic respiration
The respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen and the organic food material is incompletely oxidized into ethyl alcohol and CO2 with the little amount of energy is called anaerobic respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. Such types of respiration generally occur in lower organisms like bacteria and fungi. It also occurs in many tissues of higher plants, seeds in storage, fleshy fruits, and muscles of animals. This process of incomplete oxidation is known as fermentation in the case of bacteria and fungi.
C6H12O6→ CO2 + C2H5OH + 50kcl
Mechanism of respiration: The breakdown of organic food materials into carbon dioxide and water with the release of energy is complete in the following steps.
- Glycolysis
- Oxidative decarboxylation
- Kreb’s cycle
- Electron transport system/ Terminal oxidation
Demonstrate that carbon dioxide is evolved during fermentation.
Requirements:
Apparatus: glass rod, cotton, Kuhne’s fermentation tube, beaker, forceps, etc
Materials: yeast powder
Chemical: Sugar, water, KOH solution
Theory: Fermentation is anaerobic respiration in which incomplete oxidation of organic food material into an ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide with tittle amount of energy. It is an enzymatic process. The enzymes are produced by the metabolic activities of microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. (yeast). Alcoholic fermentation is a type of fermentation in which Sugar is converted into ethyl alcohol and CO2 with the help of enzyme zymase produced by yeast. The overall process of fermentation can be represented by the following chemical equation.
C6H12O6→CO + C2H5OH + 50kcal
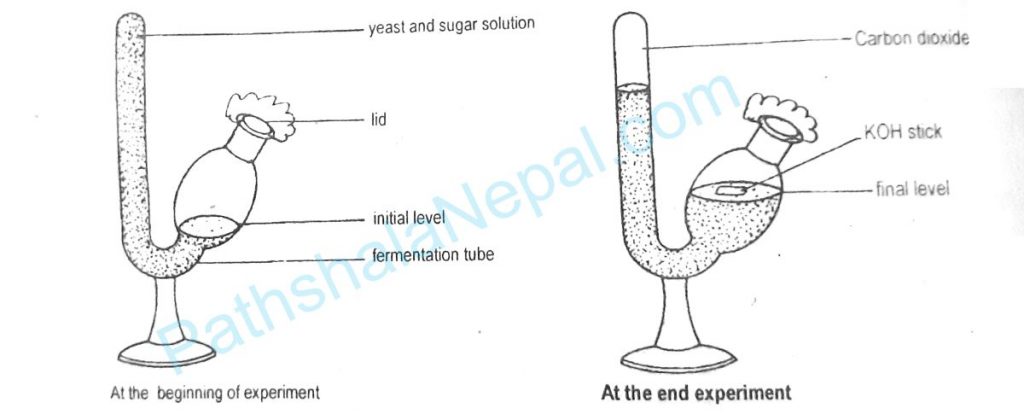
Procedure: Prepare 10% of sugar solution in beaker mix yeast powder in sugar solution. Stir the mixture with the help of a glass rod to make a homogenous mixture. Fill the vertical tube of the fermentation tube fully and bulb partially. Note the initial position of the mixture in the bulb. Cover the mouth of the bulb with a cotton plug place the experimental setup in a warm place for few hours.
Observation: After few hours gas states collecting the solution downwards. The solution level in the bulb rise. The mixture emitting an alcoholic smell. After the addition of KOH in the mixture, the solution resumes the original level in the both vertical tube and bulb.
Result of conclusion: In the homogenous mixture of sugar solution and yeast, yeast cells produce enzymes that cause the fermentation of sugar by converting it into alcohol and carbon dioxide. The released CO2 is collected at the top of the vertical tube, causes the rise in the level of mixture in the bulb. The collected gas is absorbed by KOH and a partial and partial vacuum is created in the tube. The vacuum acts as a suction pump and pulls the mixture from the bulb, resulting in the fil of mixture in the bulb and fills the empty space of the tube by solution. This confirms the evolved gas during the fermentation of carbon dioxide.
Precaution:
- Sugar and yeast powder should be mixed homogeneously.
- The vertical tube of fermentation tube should be filled completely with a mixture of sugar solution and yeast.