Define respiration and explain the experiment to demonstrate aerobic transpiration with well-labeled diagrams.
1 Answer
Respiration is the physiological process in which complete and incomplete oxidation of organic food takes place. In respiration, the oxidation of various organic food substances like carbohydrates may take place. The process of respiration occurs in all living cells of plants and animals and generally called cellular respiration. The energy produced during the process is used in all the life activities of the organisms. It is a catabolic process that occurs in mitochondria and cytoplasm of the cells and represented by the following chemical equation.
C6H12O6 + 6O2→6CO2 + H2O + Energy (2868KJor 686Kcal)
The main facts associated with respiration are
- Consumption of atmospheric oxygen.
- Release of energy by break down of organic food.
- Liberation of carbon dioxide and a small quantity of water.
- Oxidation and decomposition of reserve food.
Types of respiration: Based on the availability of oxygen during the process, respiration can be classified into two types.
- Aerobic respiration: Respiration which occurs in the presence of oxygen and organic food material is completely oxidized into CO2 and H2o with the release of energy is called aerobic respiration.
- Anaerobic respiration: The respiration which occurs in the absence of oxygen and the organic food materials is incompletely oxidized into ethyl alcohol and CO2 with a little amount of energy is called anaerobic respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm of a cell. Such types of respiration Generally occur in lower organisms like bacteria and fungi. It also occurs in many tissues of higher plants, seeds in storage, fleshy fruits, and muscles of animals. This process of incomplete oxidation is known as fermentation in the case of bacteria and fungi.
C6H12O6→CO2+ C2H5OH + 5Okcal
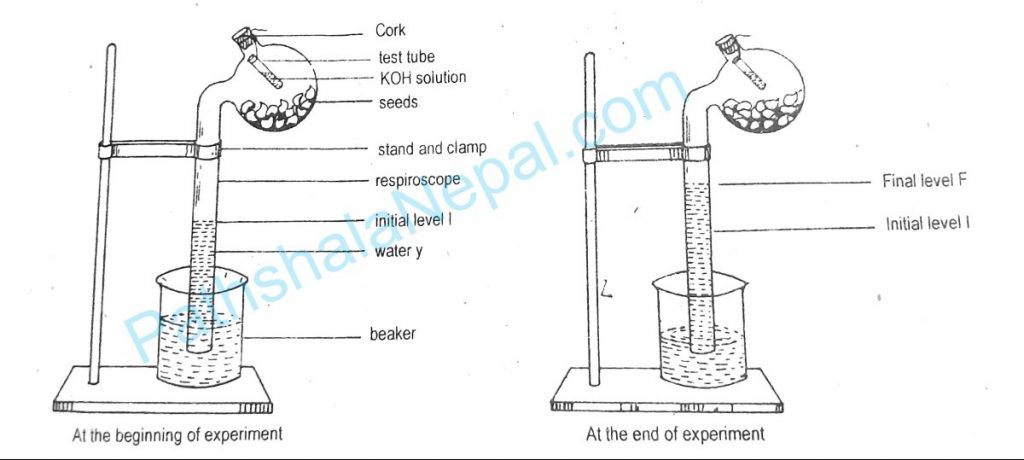
Demonstrate the process of evolution of carbon dioxide during aerobic respiration by using gagong’s respiroscope.
Requirements: Apparatus: Ganong’s respiroscope, beaker, clamped, stand, forceps, small test tube, thread.
Material: Germinating seeds of a gram.
Chemical: Water, KOH solution.
Theory: Respiration is the physiological process in which complete and incomplete oxidation of organic food takes place. In respiration, the oxidation of various organic food substances like carbohydrates may take place. The process of respiration occurs in all living cells of plants and animals and generally called cellular respiration. The energy produced during the process is used in all the life activities of the organism’s It is a catabolic process that occurs in mitochondria and cytoplasm of the cell and represented by the following chemical equation.
C6H12O6 + 6O2→6CO2 + H2O + Energy (2868KJ or 686Kcal)
The main facts associated with respiration are
- Consumption of atmospheric oxygen.
- Release of energy by break down of organic food.
- Liberation of carbon dioxide and a small quantity of water.
- Oxidation and decomposition of reserve food.
Types of respiration: Based on the availability of oxygen during the process, respiration can be classified into two types
- Aerobic respiration: Respiration which occurs in the presence of oxygen and organic food material is completely oxidized into CO2 and H2O with the release of energy is called aerobic respiration.
C6H12O6 + 6O2→6CO2 + H2O + Energy (2868KJ or 686Kcal)
- Anaerobic respiration: The respiration which occurs in the absence of oxygen and the organic food materials is incompletely oxidized into ethyl alcohol and CO2 with a little amount of energy is called anaerobic respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm of a cell. Such type of respiration generally occurs in lower organisms like bacteria and fungi. It also occurs in many tissues of higher plants, seeds in storage, fleshy fruits, and muscles of animals. This process of incomplete oxidation is known as fermentation in the case of bacteria and fungi.
C6H12O6→CO2+ C2H5OH + 5Okcal
Procedure: Take a respiroscope having a bulb with a long-bent tube. Remove the seed-coat from the germinating seeds. Place them into the bulb through its open end. Dip the bent tube into the beaker containing water. Hang a small test tube containing KOH solution with a thread inside the bulb. Close the open and tight with a cork. Fix the apparatus in a vertical position using the clamp and stand. Take an initial reading in the bent tube. Allow the setup to remain untouched for a few hours.
Observation: After few hours there is an increase in the level of water in a vertical graduated tube of respiroscope.
Result and conclusion: The geminating gram seeds placed in the bulb of respiroscope respire by utilizing oxygen present in the bulb releasing CO2 the released CO2 is absorbed by KOH and creates a partial vacuum in the bulb. The vacuum acts as a suction pump and pulls water upwards from the beaker. Thud water rises up in the vertical tube to fill the vacuum. Since KOH absorbs only CO2 gas, the evolved gas during respiration confirms CO2.
Precaution:
- Germination seeds should be used without a seed coat.
- The respiroscope should be that property.
- The end of the vertical tube should be dipped in water.
- The level of water in the graduated tube should be taken carefully.