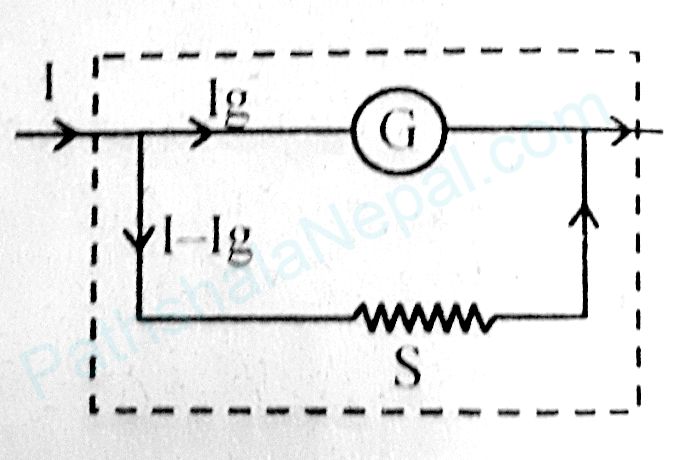
Shunt:
To convert a galvanometer into an ammeter, very low resistance is connected in parallel with a galvanometer coil so that maximum current can flow through it is called a shunt. Shunt provides an alternative path for excess current.
The value of shunt resistance S to be connected in parallel with galvanometer to convert into ammeter is \(S=\frac{I_g}{I-I_g}\times G\), where G is the resistance of galvanometer and Ig is the current flowing through it.