Joule's law of heating: Click here
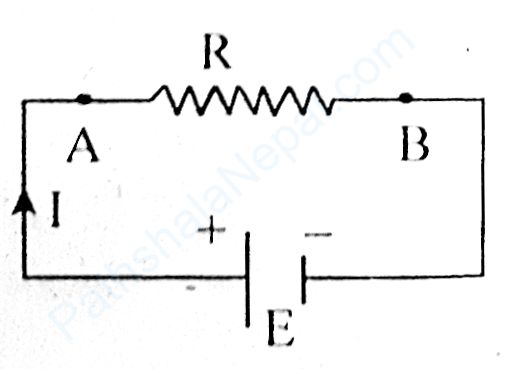
Let us consider a battery of emf E is connected across the resistance R as shown in the figure. The potential across the terminals of resistance R is V = IR, where I is the total current flow in the direction. The terminal 'A' of the resistance is connected to the positive terminal (higher potential) of the battery and terminal 'B' of the resistance is connected to the negative terminal (lower potential) of the battery.
When the charge moves from terminal A to terminal B, the net amount of work done for this is given by, W = qV
Since, q = 1t and V = IR
⇒ W = 1t × IR = \(I^2Rt\)
According to the principle of conservation of energy, this amount of work done is converted into heat energy.
i.e., Heat produced in wire = W
∴ H = I2Rt
Which is the required expression and is called Joule's law of heating.