Power
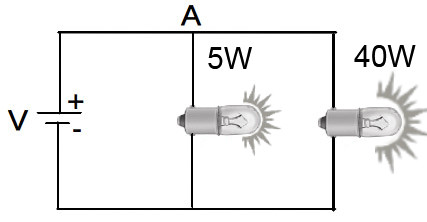
We already know that different devices and machines convert energy from one form to another form. It is not necessary that every device convert electricity at the same rate. For example consider an electric bulbs of different power, say 5 watt and 40 watt. If both bulbs are plugged in on the same circuit (house) then the heat and light energy converted from electrical energy by two bulbs are different and can be easily observed. The five watt bulb converts energy at lower rate while the 40 watt bulb convert energy at a higher rate.
Also note that the process of conversion of energy from one to another form is work done. Hence we can deduce the formula for work done as follows:
\(Power(P)=\frac{work\;done\;(W)}{time\;taken(t)})\)
If the work is done in Joule and time in second, unit of power is Joule per second or watt. If a machine can do 1 Joule work in 1 second then its power is called 1 watt. The larger units of power are kilowatt (Kw) and megawatt (Mw). The power of engines can also be measured in Horse Power (HP).
Units of Power
The most commonly used unit of power is Watt and is represented by the symbol (W). Watt is the SI unit of power. As mentioned above one joule of work done per second is watt. The unit of power watt was given in recognition of James Watt, who invented the condenser of steam engine. James watt is the first person to coin the term "Horsepower", which is the earlier accepted unit of power.
1 Watt = 1 J/s = 1 kgm2/s3
Other Units of Power
Other common units of power are ergs per second (erg/s), foot-pounbds per minute, dBm, food calories per hour or kilocaloreis per hour, horsepower (hp), BTU pe hour (BTU/h).
Units of Power Conversion
The table below shows the conversion of various units of power with respect to watt:
| Units | Symbol | Watt Equivalent |
| Horsepower | HP | 746 watts (W) |
| Kilowatts | kW | 1×103 W |
| Megawatts | MW | 1×106 W |
| Gigwatts | GW | 1×109 W |
| decibel-milliwats | dBm | 30 dBm = 1 W |
| British Thermal Unit | BTU | 3.412142 BTU/hr = 1 W |
Relation between Work, Energy & Power
Energy, work and power are interrelated to each other. In fact, the capacity of doing work is energy. When work is done on a body, its energy is increased. By the principle of conservation of energy, the energy gained by the body is equal to the energy lost during the work on it. For example, if a book on a table is moved, a work has to be done on the book. So, some energy is spent to move the book. The kinetic energy gained by the book is equal to work done on it.
We eat food for energy. Every food has energy in chemical form. When we eat food, chemical energy of the food changes into muscular energy of our body. By this energy, we can do work. When we are hungry, we feel tired and cannot do any work.
Similarly, the rate at which we can do work is called power. Power is the rate of conversion of energy. As work done in a short time interval increases, power also increases accordingly. Power may also be defined as the ratio of energy spent to the time taken to do the work. When the energy consumed in a certain time increases, power also increases and hence work is done
fast. So, work, energy and power are interrelated to each other.
- The rate of work done per second is called power. Power is also defined as the rate of conversion of energy. Power is measured in watts (W).
- If 1 Joule of work is done in 1 Sec, the power is said to be 1 Watt.
- The power of engines is also measured in Horse Power (HP). 1HP = 746Watt
This note contains Solved Questions, Formulas, and related notes.
Click Here to Read Original Version (Interactive Mode)