Introduction
When we touch a piece of ice, we feel cold. Similarly, if we touch a heated iron, we feel burning hot ( DON'T TOUCH HOT THINGS THOUGH ). Have you ever wondered why this happens?
The feeling of hot or cold is the transfer of heat energy from one body to another. When we touch a hot body we receive heat from the hot body and feel hot. Similarly, heat flows from our body to ice when we touch it. Then we feel cold. So, the flow of heat from one body to another body causes the sensation (feelings) of hot or cold.
If we rub our hands, we feel hot. Iron gets hot when rubbed against a stone. How does it happen?
Well, to know the answer to these kinds of phenomena we need to understand the nature of matter and molecules in them. A matter is composed of molecules. The molecules have potential energy stored in them. When an object is heated, it produces vibration in the molecules. Kinetic energy is produced from molecular vibration which gives rise to heat. The heat energy of a body is the total amount of kinetic energy of all molecules contained in the body. The more the molecules are vibrated, the more the body contains heat.
The degree of hotness or coldness of a body is called temperature. When we say that the body has a higher temperature we can understand that molecules of the body are vibrating intensely.
Heat and temperature
The temperature of a body increases when it is heated. Similarly, its temperature decreases when it is cooled. It means heat is the cause to increase or decrease the temperature of a body. Temperature is an effect of heat.
The difference between heat and temperature are as follows:
| SN | Heat | Temperature |
| 1. | Heat is a form of energy that gives the sensation of warmth. | Temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness of an object. |
| 2. | Heat depends on the kinetic energy of the molecules and their masses. | The temperature depends only on the kinetic energy of the molecules. |
| 3. | Heat is the cause of temperature. | Temperature is an effect of heat. |
| 4 | Heat energy is measured in Joule. | Temperature is measured in °C, °F, K |
Thermometer
We can feel the hotness of a body by touching but can't measure its degree of hotness. We use a thermometer to measure it. The thermometer is an instrument that is used for measuring the degree of hotness of a body, i.e., the temperature of the body.
Structure of Thermometer
There are various types of thermometers. Here we discuss the structure of a simple thermometer. A simple thermometer consists of a thick-walled glass tube and a capillary tube of a fine bore. Both ends are closed. A cylindrical structure is provided at one end of the tube called a bulb. The bulb has a shining white liquid metal called mercury. Mercury is a good conductor of heat since it is a metal.
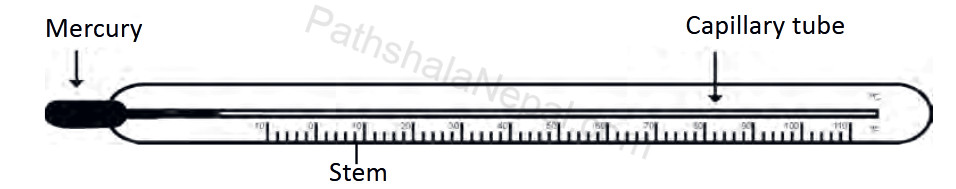
Working of Thermometer
When the bulb of a thermometer is placed in contact with a hot body, the mercury is heated and starts to expand. When it expands, its level rises in the capillary tube. If the mercury is heated more and more, its level gradually rises in the capillary tube. The temperature is measured according to the rise of mercury levels in the capillary tube. The working of the thermometer is based on the principle that "A liquid expands on heating and contracts on cooling".
Liquids used in Thermometer
Mercury
Mercury is a liquid metal. It expands uniformly on heating. It has a shiny white color so the rise and fall of mercury can be easily noticed in the capillary tube. The boiling point of mercury is 357 °C, so it is useful to measure high temperatures. As the freezing point of mercury is -39 °C, the mercury thermometer cannot be used to measure very low temperature especially in cold regions.
Alcohol
Alcohol is a colorless liquid. It expands six times greater than mercury on heating. Alcohol is quite cheaper than mercury. It can distinctly be visible by coloring. An alcohol thermometer can measure very low temperature as it melts at -115 °C. Since alcohol boils at 78 °C, it is not useful to measure higher temperatures.
Calibration of Thermometer
The process of making a scale n a thermometer in order to read the temperature is calibration. At first, two fixed points are marked in the steam.
Upper fixed point
The temperature at which pure water boils at Standard Atmospheric Pressure (i.e. 760 mmHg) is called the upper fixed point. This is 100 °C or 212 °F.
Lower fixed point
The temperature at which a piece of pure ice melts at Standard Atmospheric pressure which is 760 mm of Hg is called the lower fixed point. This is 0 °C or 32 °F
How to determine Upper and lower fixed point of a thermometer?
In order to figure out the upper fixed point of a thermometer, we need to fill about half of a Round Bottomed Flask (RB Flask) with water. Fix a thermometer and an L-Shaped glass tube through a two-holed cork on the mouth of the flask over a tripod stand with a burner as shown in the figure. The level of mercury rises as water is heated and stops at a point.
Note that there is a constant point when the water is boiling. This is the boiling point of the water (100 °C or 212 °F ) which is called the upper fixed point.
In order to determine the lower fixed point of a thermometer, fix the funnel above the beaker with the help of a clamp and stand as shown in the figure above (right side). Insert a thermometer in the ice so that its bulb can be covered with ice. The level of mercury goes down and stops. This is the melting point of water ( 0 °C or 32 °F) which is a lower fixed point.
After identifying the upper and the lower fixed points, the distance between the two points is divided into a number of equal intervals. If we choose the Celcius scale, the interval between upper and lower fixed points is divided into 100 equal parts and each part represents one degree celsius. Similarly, in Fahrenheit scale, it is divided into 180 equal parts and each part shows one degree Fahrenheit.
Unit Transformation of Temperature
Generally, there are two types of scales of temperature.
- Celcius scale: In this scale, the lower fixed point is 0 C and the upper fixed point is 100 C. The intervals are divided into 100 equal parts.
- Fahrenheit scale: In this scale, the lower fixed point is 32 F and the upper fixed point is 212 F. The intervals are divided into 180 equal parts.
The relation between Celcius and Fahrenheit scale is given by the following equation:
\(\frac{C-0}{100}=\frac{F-32}{180}\)
You can memorize the formula by looking at following structure:
\(\frac{C-lfp}{interval}=\frac{F-lfp}{interval}\) , lfp = lower fixed point and ufp = upper fixed point
Types of thermometer
There are different types of thermometers depending upon the structure and their uses.
Clinical thermometer
The thermometer which is used to measure the temperature of the human body is called the clinical thermometer. The clinical thermometer has both Celcius and Fahrenheit scales. In the Celcius scale, the stem of the thermometer is calibrated from 35C to 42 C and from 94 F to 180 F on the Fahrenheit scale. The normal human temperature is 37 C and 98.6 F.
Just above the bulb, there is a small constriction or kink in the stem. When the temperature rises, mercury can pass through the constriction but cannot pass immediately through it as the temperature falls. The mercury falls only after jerking it gently. The shape of the thermometer is not round but prismatic. Due to this shape, we can see a magnified view from a suitable angle. Nowadays, a digital clinical thermometer has been used. In this thermometer, mercury or alcohol is used.
Laboratory thermometer (simple thermometer)
It is a simple thermometer. It is simply cylindrical and long in structure. Mercury is used in this thermometer. When its bulb is placed in contact with a hot body, the volume of mercury increases, and hence the level of mercury begins to rise. And the mercury falls when its bulb is cooled. Generally, it has a temperature range from -10 C to 110 C. The capillary tube in the thermometer is made up of a fine bore and a thin-walled bulb is present so that the temperature could be measured accurately.
- Heat is the sum of the molecular kinetic energy of a body.
- The degree of hotness of a body is called temperature.
- Heat always flows from a body having a higher temperature to a body having a lower temperature.
- Heat is a cause whereas temperature is an effect.
- An instrument that is used to measure the temperature of a body is called a thermometer.
- In general, two scales are used in thermometer, celsius, and Fahrenheit.
- The thermometer used to measure the temperature of the human body is called a clinical thermometer.
- The thermometer used in the laboratory is that liquid expands of heating and contracts on cooling.
- Conversion relation of degree Celcius and degree Fahrenheit is (C-0)/100 = (F-32)/180
This note contains Solved Questions, Formulas, and related notes.
Click Here to Read Original Version (Interactive Mode)

